What is business process simulation?
Business process simulation (BPS) is a way for businesses to test, analyze, refine and optimize current business processes in a virtual environment. It enables organizations to create a digital twin of their real-world processes — an exact replica that behaves in the same way as the actual process. By simulating the flow of activities within a process, businesses can assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and predict outcomes under varying conditions.
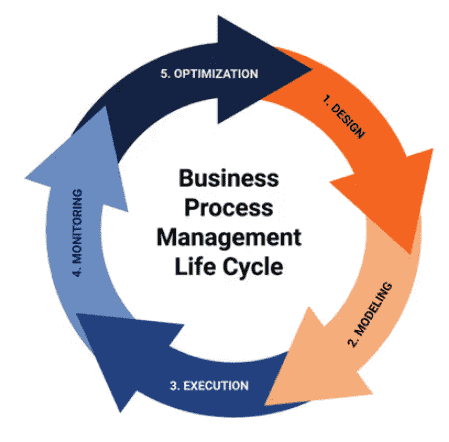
Business process simulation plays a crucial role in the Business Process Management (BPM) Life Cycle, which includes five stages — Design, Modeling, Execution, Monitoring, and Optimization — and is essential for completing the entire cycle.
In the Design and Modeling phases, you define the foundation of your process and create a virtual representation, enabling you to refine your approach before execution. These two steps are fundamental to BPS. In the Execution phase, simulation brings the model to life, providing insights into how the process performs in real time. These insights help shape the Monitoring and Optimization stages, where you can identify inefficiencies and make data-driven adjustments to continually enhance the process.
The Business Process Simulation Standard (BPSim), is widely recognized as the standard for business process simulation software. It provides a standardized framework for integrating simulation into Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) diagrams and is the core method used in Cardanit. Through BPSim, organizations can define parameters like task processing times, event triggers, and resource allocations to simulate how a process will perform in different scenarios.
Business process simulation is especially important because it enables businesses to make data-driven decisions without the risk and cost of experimenting with actual processes. It provides a safe and controlled environment to explore different scenarios and their potential effects, helping to ensure that processes operate smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal disruption to the business.
What’s the goal?
The goal of business process simulation is to accurately model real-world processes in a virtual environment to evaluate actual performance and improve it before advancing to the optimization stage. By testing and refining business processes before they are implemented in real life, organizations can better understand how changes will impact their operations. Simulation supports this goal within the broader BPM life cycle, specifically during the Execution phase, helping organizations test, execute, and analyze their processes before taking real-world action.
What are the benefits?
The benefits of business process simulation are wide-reaching and can significantly impact an organization’s performance.
-
Understand your business processes
Business process simulation helps you to gain a deeper understanding of how your processes work, highlighting key dependencies and workflows that might not be immediately obvious.
-
Identify areas for improvement
It can pinpoint inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and other issues within a process, providing clear insights into areas that need improvement.
-
Try out different scenarios
You can test various scenarios and explore the potential impact of different changes before making real-world adjustments.
-
Make informed decisions
Business process simulation provides data-driven insights, allowing you to make well-informed decisions based on how the process will perform under different conditions.
-
Improve operational efficiency
By identifying inefficiencies and optimizing workflows, business process simulation helps you streamline operations, optimize resource allocation and reduce unnecessary costs.
-
Reduce risks
Business process simulation enables you to anticipate potential risks and test solutions before implementing them, minimizing the chance of costly mistakes and unforeseen challenges.
What’s involved?
Business process simulation involves several key steps that build on one another, ensuring you get the most accurate and actionable results. Each step also ties into different stages of the BPM life cycle, helping you connect the dots between simulation and ongoing process improvement. Here’s how the process flows:
-
Define Purpose or Problem
Before starting any business process simulation, it’s critical to define the purpose clearly. What problem is your business trying to solve? What goal are you aiming to achieve? What resources — such as personnel, equipment or systems — are involved? Whether it’s optimizing an existing process, testing a new workflow, or exploring the impact of potential changes, having a well-defined purpose is essential. This clarity will guide the simulation and ensure the results are both relevant and actionable. Gathering detailed information to answer these questions is a critical part of this phase.
This aligns with the Design stage of the BPM life cycle, where the foundation of your process is established.
-
Map the process
Once the purpose is clear, the next step is to create a model that accurately reflects the business process. This model should include all relevant activities, decision points, resources, and dependencies. Using BPMN diagrams, the model should map out the flow of the process, allowing for detailed simulation of each component.
This step corresponds to the Modeling stage in the BPM life cycle, where you create a blueprint for how the process should work.
-
Collect data
Data collection is a critical to ensuring that the business process simulation is based on realistic, accurate inputs. Collect data on task durations, resource availability, costs, and other variables that could affect process performance. The more accurate the data, the more reliable the results will be.
This step ties into Execution in the BPM life cycle, where the real-world data is brought in to run the simulation.
-
Set parameters
Before running the business process simulation, set the parameters that will guide the process. Defining parameters ensures the simulation reflects real-world conditions. Review the data and assumptions gathered earlier to adjust the settings accordingly. Once the parameters are set, you’ll be ready to run the simulation.
Again, this aligns with the Execution stage, where the model is prepared and fine-tuned before being run.
-
Run the simulation
This involves executing the model with the parameters defined in a BPMN simulation software. During this step, the process will play out virtually, and the system will calculate the outcomes based on the collected data.
This step also falls under Execution, where the simulation happens, and you start to see the process in action.
-
Analyze
Now it’s time to analyze the results. Look for patterns, trends, and areas where the process performs well or struggles. Identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or risks, and consider how these might impact the real-world process. This analysis provides valuable insights into the process’s strengths and weaknesses.
This corresponds to the Monitoring stage of the BPM life cycle, where you track the performance of the process in real-time and identify areas for improvement.
-
Optimize
Based on the analysis, adjustments may need to be made to the model or data. Optimization ensures that the simulation reflects the most accurate representation of the process. This step may involve refining parameters, revising assumptions, or re-running the simulation to test different scenarios.
This aligns with the Monitoring phase in the BPM life cycle, where adjustments are made to improve the model and overall process performance.
-
Implement
After refining the model and confirming that it aligns with the business’s goals, the final step is to implement the insights gained from the simulation. This may involve adjusting the real-world process, reallocating resources, or making other operational changes to optimize performance. With the insights provided by the simulation, businesses can implement more effective strategies and improve their processes with confidence.
This final step corresponds to the Optimization stage in the BPM life cycle, where the real process is adjusted and optimized for better results.